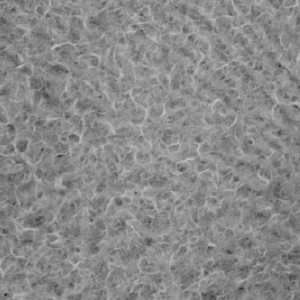
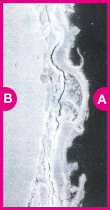
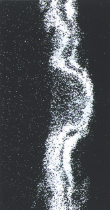
Galvanized coating layer also forms a protective film on the surface. This protective film, however, is not as fine as in ZAM™, and less adhesive (see photo at right).
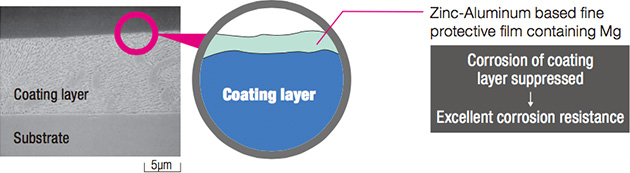
In contrast, the protective film formed on the coating surface of ZAM™ is excellent in both f inenes s and adhes ion, and consequently it inhibits permeation of cor rosion factors, preserving high corrosion resistance over a long period.
Protective film formed on the coating surface after salt spray test (4 hours)
(Thickness: 0.8 mm, coating weight: 90/90 g/m2, untreated)
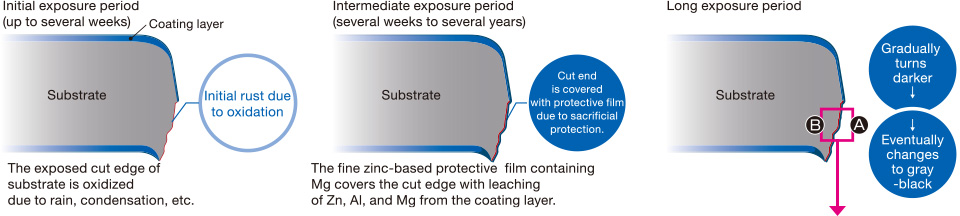
Mechanism of corrosion resistance on cut edge
Excellent corrosion resistance is achieved on cut edge parts by covering the ends with a fine zinc-based protective film that contains Al and Mg
leaching from the coating layer.
Initial period of exposure

Outdoor exposure for 3 years

(Thickness: 3.2 mm, coating weight: 150/150 g/m2, post-treatment: chromate 50 mg/m2)
Note: The color and the speed of change in color depend on sheet thicknesses and exposure environments (region, installation location, aspect, etc.).